Custom Activation Strategies
Custom activation strategies are deprecated. Please use the default activation strategy with constraints.
Custom activation strategies let you define your own activation strategies to use with Unleash. When the built-in activation strategies aren't enough, custom activation strategies are there to provide you with the flexibility you need.
Custom activation strategies work exactly like the built-in activation strategies when working in the admin UI.
Definition
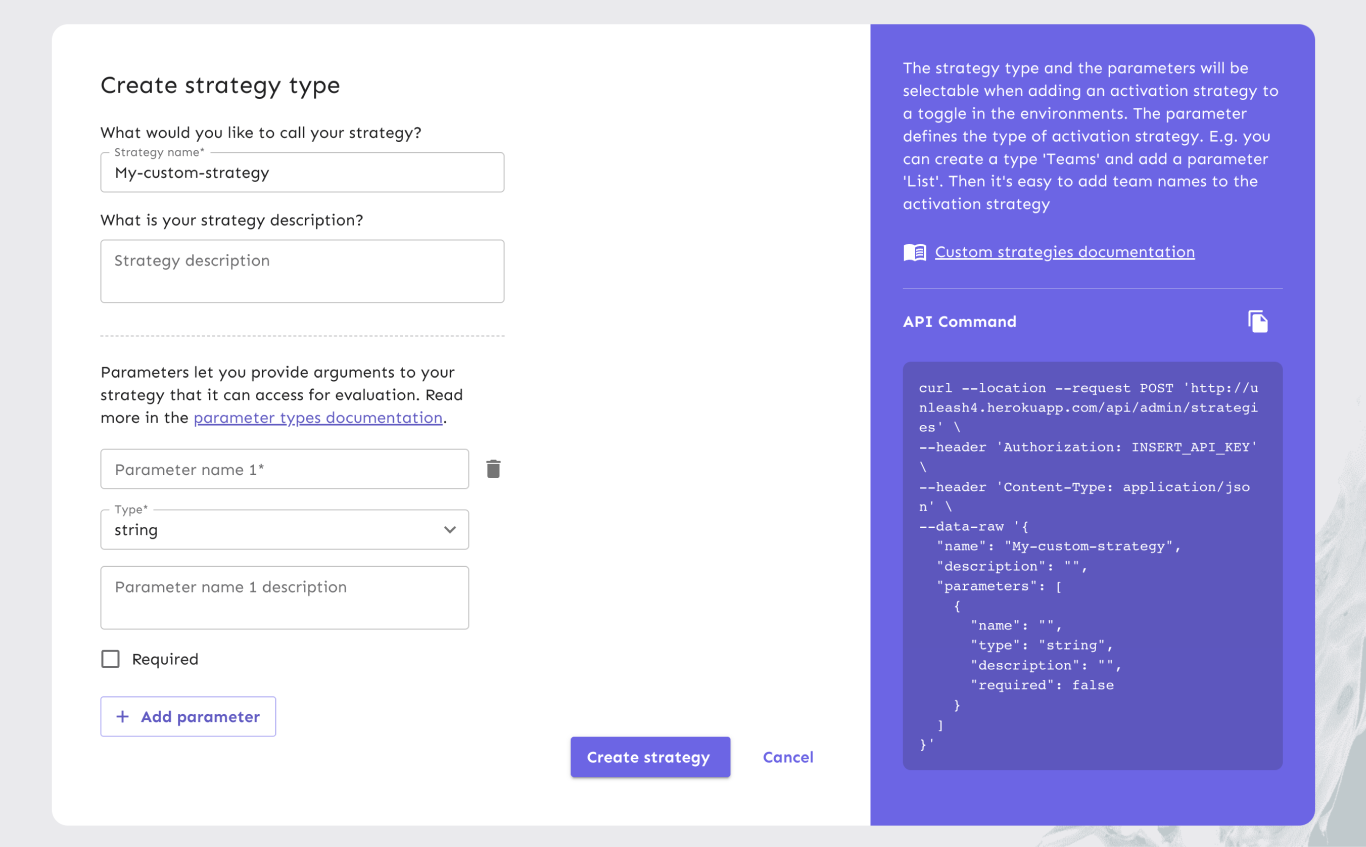
You define custom activation strategies on your Unleash instance, either via the admin UI or via the API. A strategy contains:
- A strategy name: You'll use this to refer to the strategy in the UI and in code. The strategy name should make it easy to understand what the strategy does. For instance, if a strategy uses contact numbers to determine whether a feature should be enabled, then ContactNumbers would be a good name.
- An optional description: Use this to describe what the strategy should do.
- An optional list of parameters: The parameter list lets you pass arguments to your custom activation strategy. These will be made available to your custom strategy implementation. How you interact with them differs between SDKs, but refer to the Node.js example in the how-to guide for a rough idea.
The strategy name is the only required parameter, but adding a good description will make it easier to remember what a strategy should do. The list of parameters lets you pass data from the Unleash instance to the strategy implementation.
Parameters
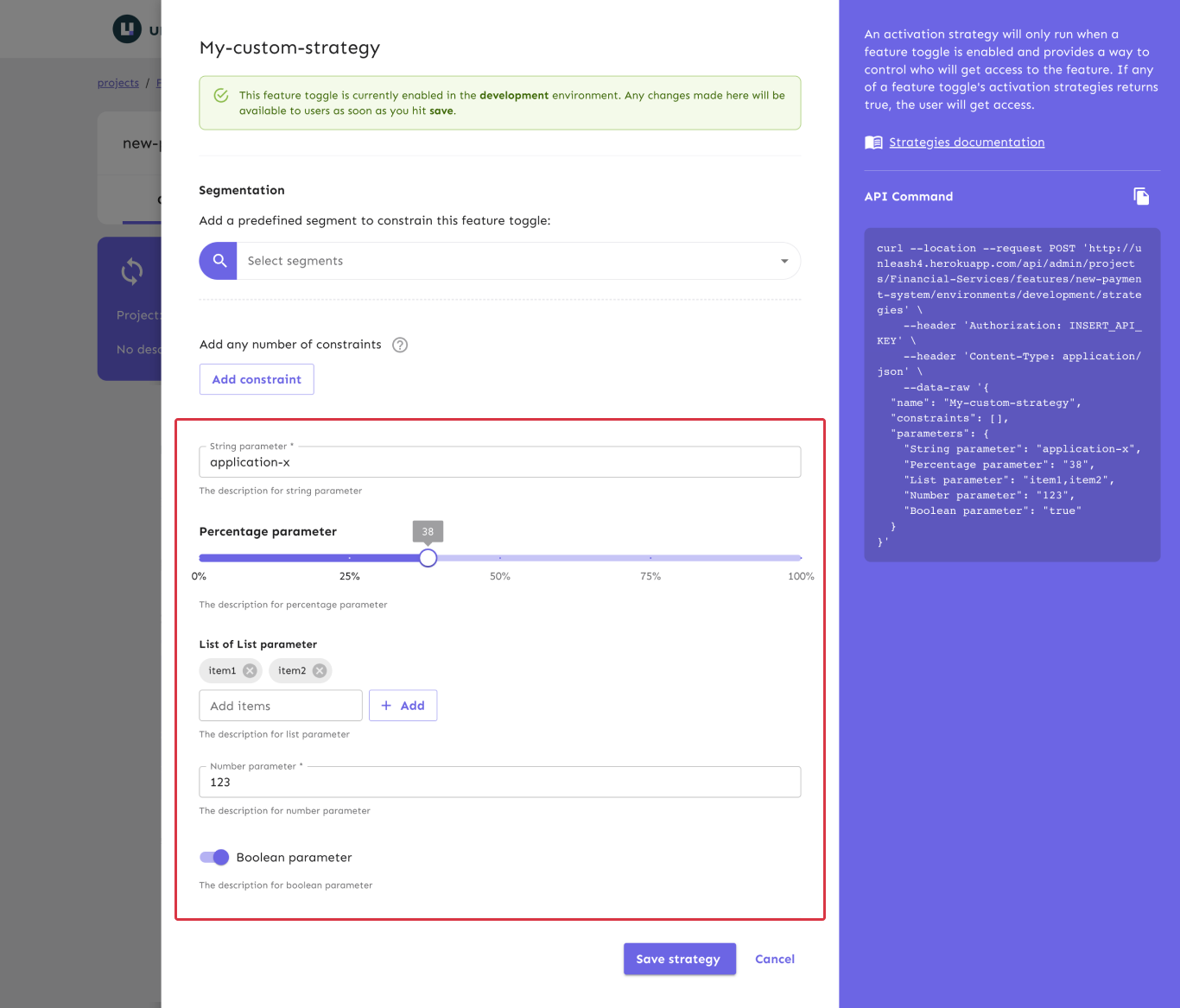
Parameters let you provide arguments to your strategy that it can access for evaluation. When creating a strategy, each parameter can be either required or optional. This marking is to help the user understand what they need to fill out; they can still save the strategy without filling out a required field.
Each parameter consists of three parts:
- a name: must be unique among the strategy's parameters.
- an optional description: describe the purpose or format of the parameter.
- a parameter type: dictates the kind of input field the user will see in the admin UI and the type of the value in the implementation code.
Parameter types
Each parameter has one of five different parameter types. A parameter's type impacts the kind of controls shown in the admin UI and how it's represented in code.
The below table lists the types and how they're represented in the JSON payload returned from the Unleash server. When parsed, the exact types will vary based on your programming language's type system.
All values have an empty string ("") as the default value. As such, if you don't interact with a control or otherwise set a value, the value will be an empty string.
| type name | code representation | example value | UI control |
|---|---|---|---|
| string | string | "a string" | A standard input field |
| percentage | a string representing a number between 0 and 100 (inclusive) | "99" | A value slider |
| list | string (values are comma-separated) | "one,two" | A multi-input text field |
| number | string | "123" | A numeric text field |
| boolean | a string: one of "true" or "false" | "true" | An on/off toggle |
Implementation
If you have not implemented the strategy in your client SDK, the check will always return false because the client doesn't recognize the strategy.
While custom strategies are defined on the Unleash server, they must be implemented on the client. All official Unleash client SDKs provide a way for you to implement custom strategies. You should refer to the individual SDK's documentation for specifics, but for an example, you can have a look at the Node.js client implementation section in the how to use custom strategies guide.
The exact method for implementing custom strategies will vary between SDKs, but the server SDKs follow the same patterns. For front-end client SDKs (Android, JavaScript, React, iOS, Flutter), the custom activation strategy must be implemented in the Unleash Proxy.
When implementing a strategy in your client, you will get access to the strategy's parameters and the Unleash Context. Again, refer to your specific SDK's documentation for more details.